Damage to the posterior cruciate ligament
A full range of orthopedic services, from diagnosis to full recovery
The posterior cruciate ligament is an important structural element of the knee joint. It & nbsp; & nbsp; stabilizes the knee joint and does not allow the lower leg to move excessively backwards.
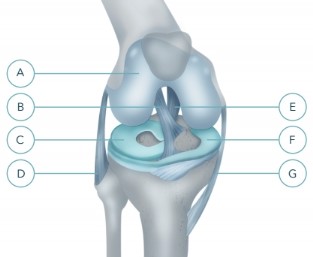
Fig. 1 Right knee joint (front view schematically without patella).
A-articular cartilage-anterior cruciate ligament
C - external (lateral) meniscus
D-peroneal (external) collateral ligament < br> E-posterior cruciate ligament
F - internal (medial) meniscus
G - tibial (internal) collateral ligament
The rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament is one of the most severe injuries to the knee joint, since the posterior cruciate ligament is a kind of "key" of the knee joint. And if the damage to the anterior cruciate ligament allows the patient to perform daily activity almost without restrictions, then with a rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament, the patient can not even walk normally.
Fortunately, the posterior cruciate ligament is torn at times less often than the anterior cruciate ligament. If all cases of damage to the ligaments of the knee joint are taken as 100 %, then from 8 to 10% will be damage to the posterior cruciate ligament.
The injury, in which the posterior cruciate ligament can be damaged, is of a high-energy nature. Most often, this happens as a result of a car accident: a blow to the front of the pedestrian's shin with the bumper of a car or a blow to the front of the driver's or passenger's shin against the displaced torpedo of the car interior. Less often in high-speed sports: when hitting an obstacle with a bent knee in alpine skiing and snowboarding; in game and contact sports when colliding with another player.
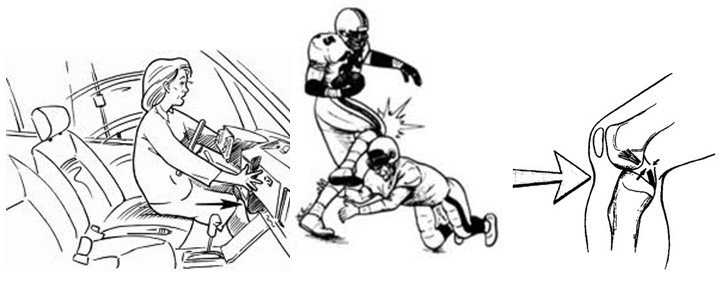 As a rule, a rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament is the cause of a dislocation of the lower leg and is often accompanied by damage to the anterior cruciate, external and internal lateral ligaments, the joint capsule, and even the vessels and nerves of the popliteal region.
As a rule, a rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament is the cause of a dislocation of the lower leg and is often accompanied by damage to the anterior cruciate, external and internal lateral ligaments, the joint capsule, and even the vessels and nerves of the popliteal region.
What are the symptoms of a torn or damaged posterior cruciate ligament?
Usually, in the acute period of ligament damage, the patient complains of pain, swelling and impaired movement in the knee joint. It should be noted that the swelling of the knee joint is not as pronounced as, for example, with damage to the anterior cruciate ligament. This is due to the fact that the posterior cruciate ligament is not completely located in the knee joint, and the bleeding that is inevitable when any ligaments are torn occurs in the popliteal region, where there is no longer a joint bag. Therefore, patients often note the appearance of a "bruise" on the back of the lower leg. The pain is quite pronounced, requires taking painkillers. Violation of movement in the knee and walking & nbsp; & nbsp; - sharp. The condition of the knee improves very slowly (over several months). Paradoxically, in patients who have been injured in a car accident, the diagnosis of a torn posterior cruciate ligament is often not established, although all of them are taken to medical institutions. This is due to the fact that the attention of doctors is focused on identifying injuries to internal organs, the skull, bone fractures, patients are often unconscious. Therefore, if there are violations in the knee joint after a traffic accident, the patient should first check the condition of the posterior cruciate ligament with a specialist.
With damage to the posterior cruciate ligament, and especially in combination with damage to the lateral ligaments, the function of the knee joint is sharply impaired. There is an abnormal displacement of the bones of the joint during each step, rapid wear of the cartilage of the kneecap and the inner half of the knee joint, and the development of severe forms of deforming arthrosis.
What is the diagnosis of a torn or damaged posterior cruciate ligament?
1. Examination of the injured joint by an orthopedic surgeon and conducting special tests to determine the degree of instability in the joint (reverse pivot shift, reverse Lachman-test, reverse driver test). As a rule, the violation of the stability of the knee with a rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament is quite rough and quite easy to detect. The exception is cases of simultaneous damage to several ligaments. The clinical diagnosis of ligament injuries in such cases requires a lot of specialist experience.
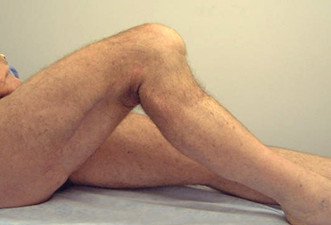
Sharp sinking of the lower leg in the posterior cruciate ligament rupture
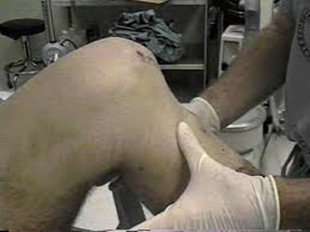
Positive & nbsp; reverse driver test
2. Radiography of the knee joint does not reveal the actual damage to the posterior cruciate ligament, except in cases of its separation with a bone fragment. However, when analyzing radiographs, it is possible to note both the abnormal position of the joint bones relative to each other, and tear-off fractures caused by damage to other ligaments, most often the external collateral. 3. Ultrasound examination of the knee joint in the case of a torn posterior cruciate ligament is not sufficiently informative.
4. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is the leading method for diagnosing posterior cruciate ligament injuries. However, it should be noted that with the help of a single MRI with simultaneous damage to several ligaments, the diagnosis can be quite difficult to establish. In this case, an experienced surgeon should simultaneously perform a clinical diagnosis and study the MRI data.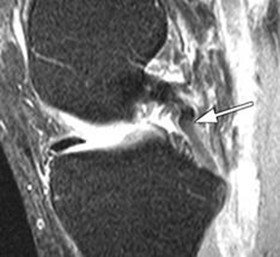
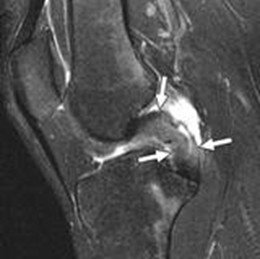
5. Diagnostic arthroscopy is the most accurate method of diagnosing knee ligament injuries. To do this, through small punctures, an arthroscope is inserted into the joint cavity, at the end of which there is a video camera, through which the doctor sees all the structures of the joint, assesses their integrity and functional state.Arthroscopy is a therapeutic and diagnostic method, since after a full examination and the establishment of a final diagnosis, surgical treatment is performed.
What is the treatment for a torn or damaged posterior cruciate ligament?
1. Conservative treatment.
Since the posterior cruciate ligament is located mainly out of joint, in the area of good blood circulation, the stabilization of the joint with a plaster or polymer bandage, anti-inflammatory and decongestant therapy, wearing crutches to relieve the load from the damaged joint can lead to the fusion of torn fragments. Usually, these measures are carried out during the acute period of the injury, allowing you not to perform surgery to restore the posterior cruciate ligament, which is justified, for example, in a serious general condition of the victim. Often, conservative treatment leads to satisfactory results. However, damage to the posterior cruciate ligament in athletes requires immediate surgical treatment, since only then can the full restoration of knee function and athletic fitness be guaranteed.
2. Surgical treatment.
A common wide-access operation requires large incisions and opening of the joint. This is quite traumatic for patients, which requires a longer hospital stay – 7 days or more, more serious rehabilitation, and a longer recovery period after surgery. In cases where it is necessary to simultaneously perform the restoration of the posterior cruciate ligament and surgery for intra-articular bone fractures, we still resort to open access. 3. Plastic surgery of the ligament under arthroscopic control.
Arthroscopy is a modern, low-traumatic method of surgical treatment of ligament injuries and ruptures. Arthroscopy does not require large incisions and opening of the joint, as with conventional surgical treatment, which allows you to less injure the patient, reduce the period of his stay in the hospital to 2-3 days, quickly return him to an active lifestyle.
What is the treatment of injuries of the cruciate ligaments offers our medical center?
For the treatment of injuries and ruptures of the posterior cruciate ligament, we perform ligament repair under arthroscopic control. Arthroscopy – operation "without incision". Instead of an incision, local mini-punctures are performed, in one of which an arthroscope with a video camera is inserted, and in the other the tools for performing the operation.The image from the video camera is zoomed in on the video monitor, which allows the doctor to examine in detail all the structures of the joint and identify damage to the ligament.

Fig. 1 Right knee joint (front view schematically without patella).
A-articular cartilage-anterior cruciate ligament
C - external (lateral) meniscus
D-peroneal (external) collateral ligament < br> E-posterior cruciate ligament
F - internal (medial) meniscus
G - tibial (internal) collateral ligament
The rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament is one of the most severe injuries to the knee joint, since the posterior cruciate ligament is a kind of "key" of the knee joint. And if the damage to the anterior cruciate ligament allows the patient to perform daily activity almost without restrictions, then with a rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament, the patient can not even walk normally.
Fortunately, the posterior cruciate ligament is torn at times less often than the anterior cruciate ligament. If all cases of damage to the ligaments of the knee joint are taken as 100 %, then from 8 to 10% will be damage to the posterior cruciate ligament.
The injury, in which the posterior cruciate ligament can be damaged, is of a high-energy nature. Most often, this happens as a result of a car accident: a blow to the front of the pedestrian's shin with the bumper of a car or a blow to the front of the driver's or passenger's shin against the displaced torpedo of the car interior. Less often in high-speed sports: when hitting an obstacle with a bent knee in alpine skiing and snowboarding; in game and contact sports when colliding with another player.
 As a rule, a rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament is the cause of a dislocation of the lower leg and is often accompanied by damage to the anterior cruciate, external and internal lateral ligaments, the joint capsule, and even the vessels and nerves of the popliteal region.
As a rule, a rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament is the cause of a dislocation of the lower leg and is often accompanied by damage to the anterior cruciate, external and internal lateral ligaments, the joint capsule, and even the vessels and nerves of the popliteal region. What are the symptoms of a torn or damaged posterior cruciate ligament?
Usually, in the acute period of ligament damage, the patient complains of pain, swelling and impaired movement in the knee joint. It should be noted that the swelling of the knee joint is not as pronounced as, for example, with damage to the anterior cruciate ligament. This is due to the fact that the posterior cruciate ligament is not completely located in the knee joint, and the bleeding that is inevitable when any ligaments are torn occurs in the popliteal region, where there is no longer a joint bag. Therefore, patients often note the appearance of a "bruise" on the back of the lower leg. The pain is quite pronounced, requires taking painkillers. Violation of movement in the knee and walking & nbsp; & nbsp; - sharp. The condition of the knee improves very slowly (over several months). Paradoxically, in patients who have been injured in a car accident, the diagnosis of a torn posterior cruciate ligament is often not established, although all of them are taken to medical institutions. This is due to the fact that the attention of doctors is focused on identifying injuries to internal organs, the skull, bone fractures, patients are often unconscious. Therefore, if there are violations in the knee joint after a traffic accident, the patient should first check the condition of the posterior cruciate ligament with a specialist.
With damage to the posterior cruciate ligament, and especially in combination with damage to the lateral ligaments, the function of the knee joint is sharply impaired. There is an abnormal displacement of the bones of the joint during each step, rapid wear of the cartilage of the kneecap and the inner half of the knee joint, and the development of severe forms of deforming arthrosis.
What is the diagnosis of a torn or damaged posterior cruciate ligament?
1. Examination of the injured joint by an orthopedic surgeon and conducting special tests to determine the degree of instability in the joint (reverse pivot shift, reverse Lachman-test, reverse driver test). As a rule, the violation of the stability of the knee with a rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament is quite rough and quite easy to detect. The exception is cases of simultaneous damage to several ligaments. The clinical diagnosis of ligament injuries in such cases requires a lot of specialist experience.

Sharp sinking of the lower leg in the posterior cruciate ligament rupture

Positive & nbsp; reverse driver test
2. Radiography of the knee joint does not reveal the actual damage to the posterior cruciate ligament, except in cases of its separation with a bone fragment. However, when analyzing radiographs, it is possible to note both the abnormal position of the joint bones relative to each other, and tear-off fractures caused by damage to other ligaments, most often the external collateral. 3. Ultrasound examination of the knee joint in the case of a torn posterior cruciate ligament is not sufficiently informative.
4. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is the leading method for diagnosing posterior cruciate ligament injuries. However, it should be noted that with the help of a single MRI with simultaneous damage to several ligaments, the diagnosis can be quite difficult to establish. In this case, an experienced surgeon should simultaneously perform a clinical diagnosis and study the MRI data.


5. Diagnostic arthroscopy is the most accurate method of diagnosing knee ligament injuries. To do this, through small punctures, an arthroscope is inserted into the joint cavity, at the end of which there is a video camera, through which the doctor sees all the structures of the joint, assesses their integrity and functional state.Arthroscopy is a therapeutic and diagnostic method, since after a full examination and the establishment of a final diagnosis, surgical treatment is performed.
What is the treatment for a torn or damaged posterior cruciate ligament?
1. Conservative treatment.
Since the posterior cruciate ligament is located mainly out of joint, in the area of good blood circulation, the stabilization of the joint with a plaster or polymer bandage, anti-inflammatory and decongestant therapy, wearing crutches to relieve the load from the damaged joint can lead to the fusion of torn fragments. Usually, these measures are carried out during the acute period of the injury, allowing you not to perform surgery to restore the posterior cruciate ligament, which is justified, for example, in a serious general condition of the victim. Often, conservative treatment leads to satisfactory results. However, damage to the posterior cruciate ligament in athletes requires immediate surgical treatment, since only then can the full restoration of knee function and athletic fitness be guaranteed.
2. Surgical treatment.
A common wide-access operation requires large incisions and opening of the joint. This is quite traumatic for patients, which requires a longer hospital stay – 7 days or more, more serious rehabilitation, and a longer recovery period after surgery. In cases where it is necessary to simultaneously perform the restoration of the posterior cruciate ligament and surgery for intra-articular bone fractures, we still resort to open access. 3. Plastic surgery of the ligament under arthroscopic control.
Arthroscopy is a modern, low-traumatic method of surgical treatment of ligament injuries and ruptures. Arthroscopy does not require large incisions and opening of the joint, as with conventional surgical treatment, which allows you to less injure the patient, reduce the period of his stay in the hospital to 2-3 days, quickly return him to an active lifestyle.
What is the treatment of injuries of the cruciate ligaments offers our medical center?
For the treatment of injuries and ruptures of the posterior cruciate ligament, we perform ligament repair under arthroscopic control. Arthroscopy – operation "without incision". Instead of an incision, local mini-punctures are performed, in one of which an arthroscope with a video camera is inserted, and in the other the tools for performing the operation.The image from the video camera is zoomed in on the video monitor, which allows the doctor to examine in detail all the structures of the joint and identify damage to the ligament.
Product rating is: 0 from 5
Please rate the product:
Advantages of treatment in Orthopedics by Ruslan Sergienko
-
10 years on medical services in Ukraine
-
> 25 years of experience with leading specialists
-
Anna Vovchenko and Ruslan Sergienko are recognized opinion leaders among the orthopedic traumatologists
-
> 150,000 consultations were held
-
> 7,500 surgeries were performed
-
All types of pain management
-
The operating unit is equipped according to international standards
-
Availability of all medicines and supplies
-
Single rooms, equipped with the characteristics of orthopedic patients
-
Three meals a day
-
Postoperative rehabilitation by certified specialists
-
Pricing Transparency
