Anterior cruciate ligament injury
A full range of orthopedic services, from diagnosis to full recovery
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is an anatomical entity in the middle of the knee joint between the femur and tibia.
PKS:
mechanically holds the bones from the mutual offset;
takes the main part in the spatial orientation of the knee joint by activating the appropriate limb muscles through neuromuscular transmission that allows us to perform complex movement "in automatic mode".
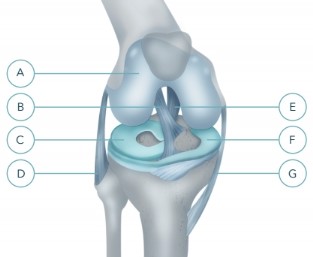
A - articular cartilage
B - anterior cruciate ligament
C - external (lateral) meniscus
D - peroneal (external) collateral ligament
E - posterior cruciate ligament
F - internal (medial) meniscus
G - tibial (inner) collateral ligament
Question: can the knee to function properly without PX?
No. An ACL rupture is the destruction of the mechanical connection between the bones of the knee joint. There is instability, accompanied by the appearance of abnormal displacements in the joint, injury to intra-articular structures, including cartilage.
Knee gradually (for 7 - 11 years) is destroyed.
Lost "automatic control" in the position of the limb - control knee goes into "manual mode", there is a need to continuously monitor the position of the knee joint.
This control is only possible with constant tension of the muscles around the joint and performing simple movements (e.g., walking on level ground).
Any sudden movement can cause loss of control and buscontroller the displacement of the bones in the joint with simultaneous injury to the menisci and cartilage.
Therefore, to restore the full function of the joint without reconnection is impossible.
Question: is it possible for the restoration of anterior cruciate ligament rehabilitation?
Rehabilitation can improve the ability of the patient to manage defective knee. By constantly training the patient may even start to run (in the absence of PKS is absolutely contraindicated) on a flat surface and a direction.
However, running (and often walk) it is possible to first slip or need the reflex to dramatically change the direction of movement (for example, in the event of unexpected interference).
Thus, if the patient chooses a very careful method of physical activity, to move without PKS possible, but inevitable loss of quality of life.<br>
Question: is it True that arthritis develops as the operated and not operated patients?
Yes, it's true. Osteoarthritis starts immediately after injury and is not the result of the operation.
Operative intervention can significantly slow down the development of arthritis, while maintaining activity and quality of life. The patient starts to treat arthritis in older age.
The failure of the operation will lead to the development of osteoarthritis in 7 - 11 years old, and all this time the patient will be afraid of any activity.
Issue: whether during the operation, joined to the broken PCP?
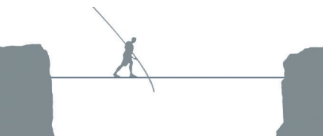
In the event of termination of the rope in the figure is unlikely to sew it securely.
Technically stitching PKS possible, but the strength of the weld is debatable.
More reliably to push and fasten the new cable. Also, the torn ACL is replaced with a graft.
Question: what happens during surgery to replace the PCB?
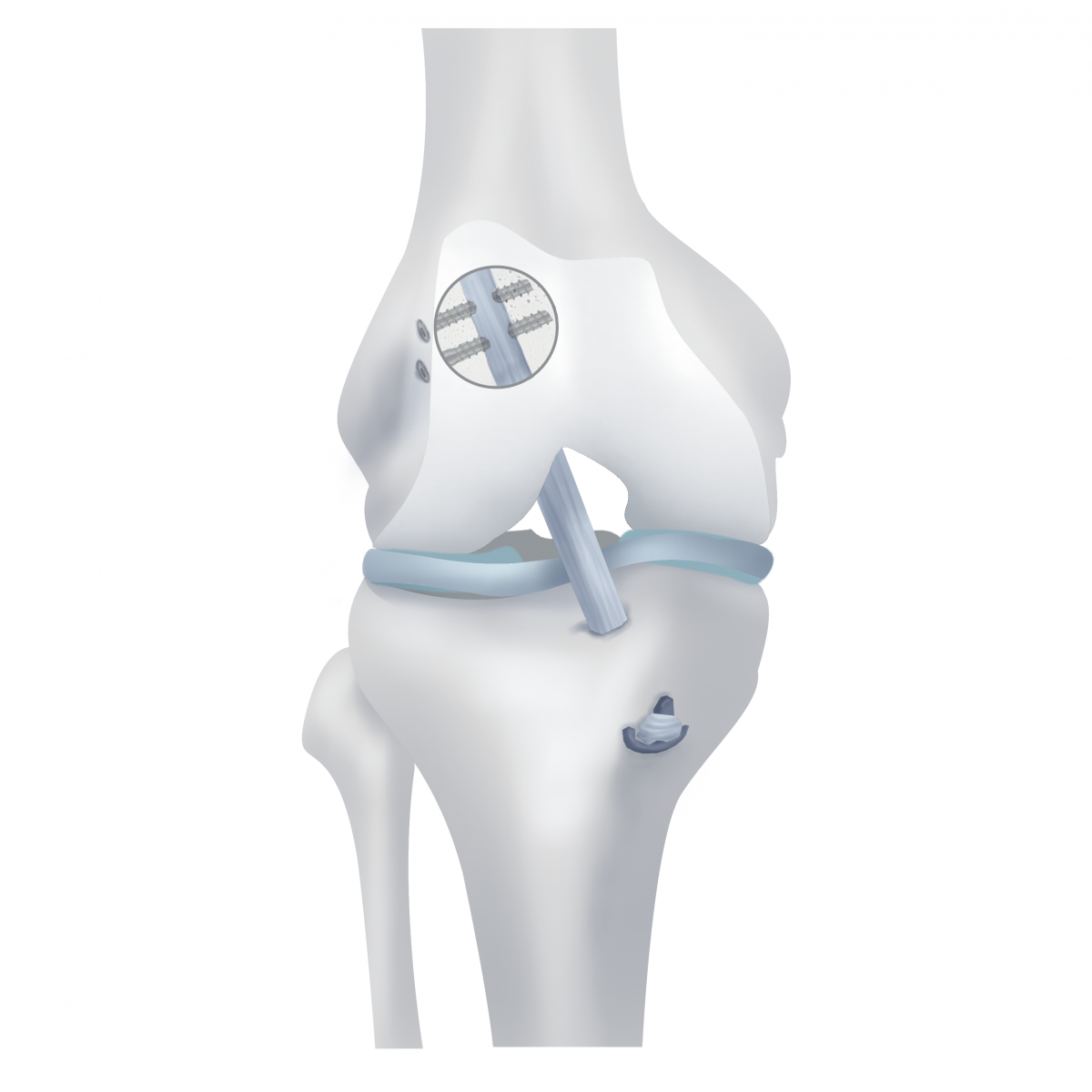
Replacement the PCB is held under the control of the camcorder entered into the cavity of the knee joint through punctures, that is, arthroscopic control. In femoral and tibial bones using special tools are tunnels in pre-visit PCP.
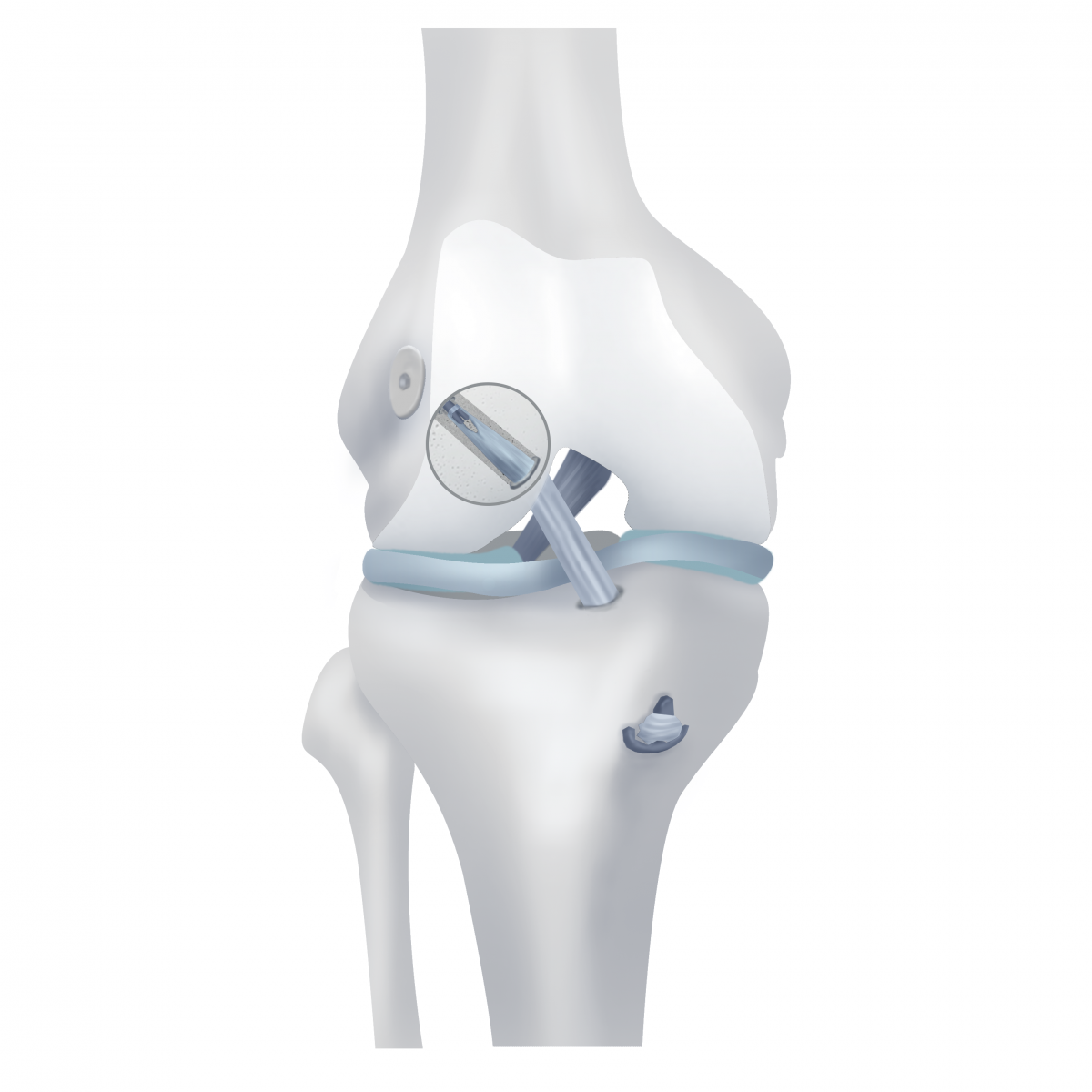
New artificially created ligament (graft) is pulled into the tunnel and fixed to ensure good contact with the bone and further splicing between them.
Question: where can I get a new connection for my knee?
An allograft (donor ligament).
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Synthetic graft.
Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Q: what is the graft in orthopaedic practice to use the most?
Autograft used in the vast majority of updates PKS in the world.
The allograft used for repeated surgical interventions in young people.
Synthetic transplantati used mainly in older persons.
Question: when the human body take tissue for autograft?
Use of the tendon of the various muscles of the thigh and lower leg, taking the graft without bone blocks, and one or two bone blocks. Various muscles perform different function, so the final decision is taken in each case individually based on the level and characteristics of physical activity that the patient is planning to have after recovery.
In our clinic we have extensive experience of working with professional athletes, so they often work with unpopular among orthopedists transplants (in particular, the tendon of the quadriceps femoris), adapting to the characteristics of a sport, so as not to damage the main activities for this group of muscles, and take a graft of muscle that is involved is minimal.
Examples of different autografts:
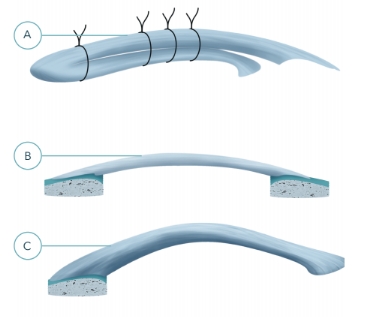
A transplant of tendon polyoxazolines and tender muscles (ST + GT) without bone blocks
B - a transplant from his own patellar tendon with two bone blocks (BTB)
C - transplant of the quadriceps tendon (QT)
Graft ST + GT.
Almost 2 times stronger than the anterior cruciate ligament, which doesn't make sense. Has a circular cross section in contrast to the flat in the natural PKS.
After the establishment of the stretch, which affects the result of the operation.
Splicing of tendon to bone is not 100% guaranteed.
The fibers of the tendons that form the graft, never fused with each other, there were separate even after the fusion of the bones.
Often soreness at the site of a transplant, loss of function of the leg (especially acceleration).
BTB grafts and QT.
Strength equal to the PCB. Do not stretch.
Splicing blocks of bone with bone 100% guaranteed.
Both grafts is monofilament, the cross section is flat, as in the natural PKS.
Compared with the ST + GT no pain at the intake and loss of function.
The disadvantage for the doctor is the complexity of the fence and the installation of these grafts compared with ST + GT.
Question: as the graft is fixed in the middle of the joint?
Response: today in operative Orthopaedics possible to use the three versions of fixation:
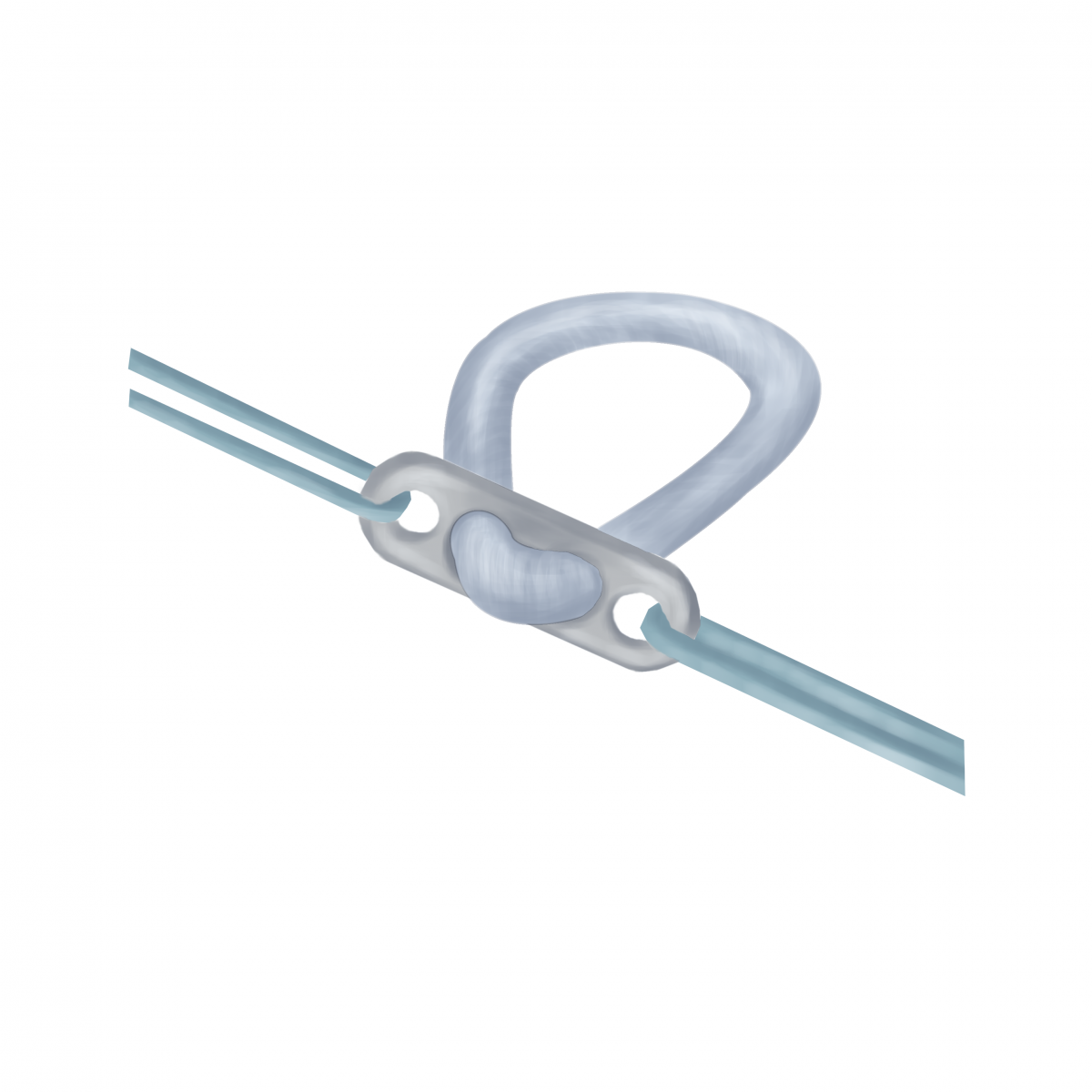
suture loop
the locking rods
interference screws:
Disadvantages of fixation suture loop:
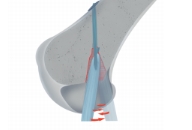
The unreliability of contact with the wall of the femoral tunnel, breaking walls (the wiper).
The constant presence of a metal latch and a thick synthetic strips in the body.
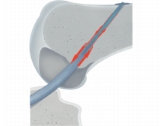
The possibility of translational movement in the channels (the banjo).
Fixation suture loop really is the most durable, but this does not make sense if such a fixation is applied on only one side (on the femur), and the other side is installed with an interference screw.
Disadvantages of fixing the locking rod
It is natural to place the tunnel in the femur is very difficult, often impossible.
The unreliability of contact with the wall of the femoral tunnel (a small square) and the possibility of breaking its walls (the wiper).
Fixation with an interference screw
In our clinic offers the advantage of the use of the graft tendon of the quadriceps femoris (QT) fixation with interference screws. It is technically more complicated technique, it requires the skill of surgeons and additional special equipment. In Ukraine, in addition to our clinic, rarely used. We have the technique perfectly, since it has many advantages over the others for the final result of the operation for the patient.
In patients with possible disruption of the microcirculation (Smoking, diabetes, etc.) and re-sculpting procedures PKS we use the BTB graft with two bone blocks.
Q: what is the period after injury is possible to do the operation?
In the absence of a pronounced inflammatory process and restrictions of movement in the joints in any period.
Question: is this a painful procedure?
The operation is painless thanks to the use in our clinic, the combined method of anesthesia: spinal anesthesia and blocking of nerve endings on the thigh. During surgical intervention introduces a sleeping pill. Postoperative analgesia is used according to need.
Question: how long is the operation?
The technical part of the replacement the PCB only lasts about 45 minutes.
Question: how much should you be in the hospital?
2 days.
Question: when may stepped on the foot after surgery?
Step on the operated leg with a partial load with the help of crutches is allowed on the next day after surgery. Crutches are used to unloading of the limb for 4 weeks after the operation.
Question: is fixed leg in a cast?
No. Uses removable retaining device (splint), which should be worn for 4 weeks at night and during the movement. If the limb is not loaded (the man sits or lies), the splint is not used.
Question: how soon after surgery can normally walk?
As a rule, the normal gait is restored within 6 weeks after surgery.
Question: when is allowed to drive a car?
Question: when can you return to sports?
Question: what is the effectiveness of surgery?
If the operation is OK, restore the function of the knee joint and preliminary quality of life possible almost in 100% of cases.
However, there is no 100% guarantee any form of treatment.
According to our clinic, we obtained excellent and good results plastic surgery PCP in 96.2% of cases.
Satisfactory results - 3.2% of cases.
Unsatisfactory (resorption of the transplant, recurrence of instability) - 0.6%
The result depends on many components, which include:
Thus, to do surgery for ACL reconstruction in specialized clinics definitely worth it.
Question: possible complications?
In our clinic, it was noted the following problems:
Reactive arthritis - inflammation in the knee joint in 2 - 3 weeks after surgery as a result of entering into the joint private microorganisms with undetected foci of chronic inflammation. Frequency - 1 in more than 50 operations. Treated with antibiotics.
Arthrofibrosis - the increase in terms of achieving full range of motion in the joint due to excessive formation of scar tissue. Treated with strengthening and rehabilitation exercises. In the absence of progression of range of motion after 4.5 months after operation, a dissection of scars with the help of arthroscopic surgery. The frequency of repeated operations - 1 in more than 50 operations.
Question: what are the advantages of treatment in the medical center "Orthopedics Ruslan Sergienko"?
ENTRUST THE CARE OF THEIR HEALTH REAL PROFESSIONALS!
PKS:
mechanically holds the bones from the mutual offset;
takes the main part in the spatial orientation of the knee joint by activating the appropriate limb muscles through neuromuscular transmission that allows us to perform complex movement "in automatic mode".

A - articular cartilage
B - anterior cruciate ligament
C - external (lateral) meniscus
D - peroneal (external) collateral ligament
E - posterior cruciate ligament
F - internal (medial) meniscus
G - tibial (inner) collateral ligament
Question: can the knee to function properly without PX?
No. An ACL rupture is the destruction of the mechanical connection between the bones of the knee joint. There is instability, accompanied by the appearance of abnormal displacements in the joint, injury to intra-articular structures, including cartilage.
Knee gradually (for 7 - 11 years) is destroyed.
Lost "automatic control" in the position of the limb - control knee goes into "manual mode", there is a need to continuously monitor the position of the knee joint.
This control is only possible with constant tension of the muscles around the joint and performing simple movements (e.g., walking on level ground).
Any sudden movement can cause loss of control and buscontroller the displacement of the bones in the joint with simultaneous injury to the menisci and cartilage.
Therefore, to restore the full function of the joint without reconnection is impossible.
Question: is it possible for the restoration of anterior cruciate ligament rehabilitation?
Rehabilitation can improve the ability of the patient to manage defective knee. By constantly training the patient may even start to run (in the absence of PKS is absolutely contraindicated) on a flat surface and a direction.
However, running (and often walk) it is possible to first slip or need the reflex to dramatically change the direction of movement (for example, in the event of unexpected interference).
Thus, if the patient chooses a very careful method of physical activity, to move without PKS possible, but inevitable loss of quality of life.<br>
Question: is it True that arthritis develops as the operated and not operated patients?
Yes, it's true. Osteoarthritis starts immediately after injury and is not the result of the operation.
Operative intervention can significantly slow down the development of arthritis, while maintaining activity and quality of life. The patient starts to treat arthritis in older age.
The failure of the operation will lead to the development of osteoarthritis in 7 - 11 years old, and all this time the patient will be afraid of any activity.
Issue: whether during the operation, joined to the broken PCP?

In the event of termination of the rope in the figure is unlikely to sew it securely.
Technically stitching PKS possible, but the strength of the weld is debatable.
More reliably to push and fasten the new cable. Also, the torn ACL is replaced with a graft.
Question: what happens during surgery to replace the PCB?
Replacement the PCB is held under the control of the camcorder entered into the cavity of the knee joint through punctures, that is, arthroscopic control. In femoral and tibial bones using special tools are tunnels in pre-visit PCP.

New artificially created ligament (graft) is pulled into the tunnel and fixed to ensure good contact with the bone and further splicing between them.
Question: where can I get a new connection for my knee?

- the allograft - a bunch of the other person - a donor
- synthetic grafts;
- autograft - a patient's own tissue, a fence which create a connection occur during the primary operation
An allograft (donor ligament).
Advantages:
- no need to pick up the tendon of the patient;
- the decrease of operation time.
Disadvantages:
- the increase in the cost of the intervention (+ 51 000 UAH)
- immunological reaction, which weakens the transplant after his fusion with the bones;
- the possibility of infection (HIV, hepatitis, etc.).
Synthetic graft.
- no need to pick up the tendon of the patient;
- the decrease of operation time;
- it is possible to load.
Disadvantages:
- ncreasing the value of interference
- the inability to fusion with the bones - small strength of fixation;
- the necessity of application of metal clips;
- limited lifetime (due to the limited number of cycles of flexion-extension).
Advantages:
- the possibility of full integration with the restoration of blood flow;
- does not increase the cost of the operation;
- no risk of infection.
Disadvantages:
- tissue damage in places a transplant.
Q: what is the graft in orthopaedic practice to use the most?
Autograft used in the vast majority of updates PKS in the world.
The allograft used for repeated surgical interventions in young people.
Synthetic transplantati used mainly in older persons.
Question: when the human body take tissue for autograft?
Use of the tendon of the various muscles of the thigh and lower leg, taking the graft without bone blocks, and one or two bone blocks. Various muscles perform different function, so the final decision is taken in each case individually based on the level and characteristics of physical activity that the patient is planning to have after recovery.
In our clinic we have extensive experience of working with professional athletes, so they often work with unpopular among orthopedists transplants (in particular, the tendon of the quadriceps femoris), adapting to the characteristics of a sport, so as not to damage the main activities for this group of muscles, and take a graft of muscle that is involved is minimal.
Examples of different autografts:

A transplant of tendon polyoxazolines and tender muscles (ST + GT) without bone blocks
B - a transplant from his own patellar tendon with two bone blocks (BTB)
C - transplant of the quadriceps tendon (QT)
Graft ST + GT.
Almost 2 times stronger than the anterior cruciate ligament, which doesn't make sense. Has a circular cross section in contrast to the flat in the natural PKS.
After the establishment of the stretch, which affects the result of the operation.
Splicing of tendon to bone is not 100% guaranteed.
The fibers of the tendons that form the graft, never fused with each other, there were separate even after the fusion of the bones.
Often soreness at the site of a transplant, loss of function of the leg (especially acceleration).
BTB grafts and QT.
Strength equal to the PCB. Do not stretch.
Splicing blocks of bone with bone 100% guaranteed.
Both grafts is monofilament, the cross section is flat, as in the natural PKS.
Compared with the ST + GT no pain at the intake and loss of function.
The disadvantage for the doctor is the complexity of the fence and the installation of these grafts compared with ST + GT.
Question: as the graft is fixed in the middle of the joint?
Response: today in operative Orthopaedics possible to use the three versions of fixation:
suture loop

the locking rods

interference screws:

Disadvantages of fixation suture loop:

The unreliability of contact with the wall of the femoral tunnel, breaking walls (the wiper).
The constant presence of a metal latch and a thick synthetic strips in the body.

The possibility of translational movement in the channels (the banjo).
Fixation suture loop really is the most durable, but this does not make sense if such a fixation is applied on only one side (on the femur), and the other side is installed with an interference screw.
Disadvantages of fixing the locking rod
It is natural to place the tunnel in the femur is very difficult, often impossible.
The unreliability of contact with the wall of the femoral tunnel (a small square) and the possibility of breaking its walls (the wiper).
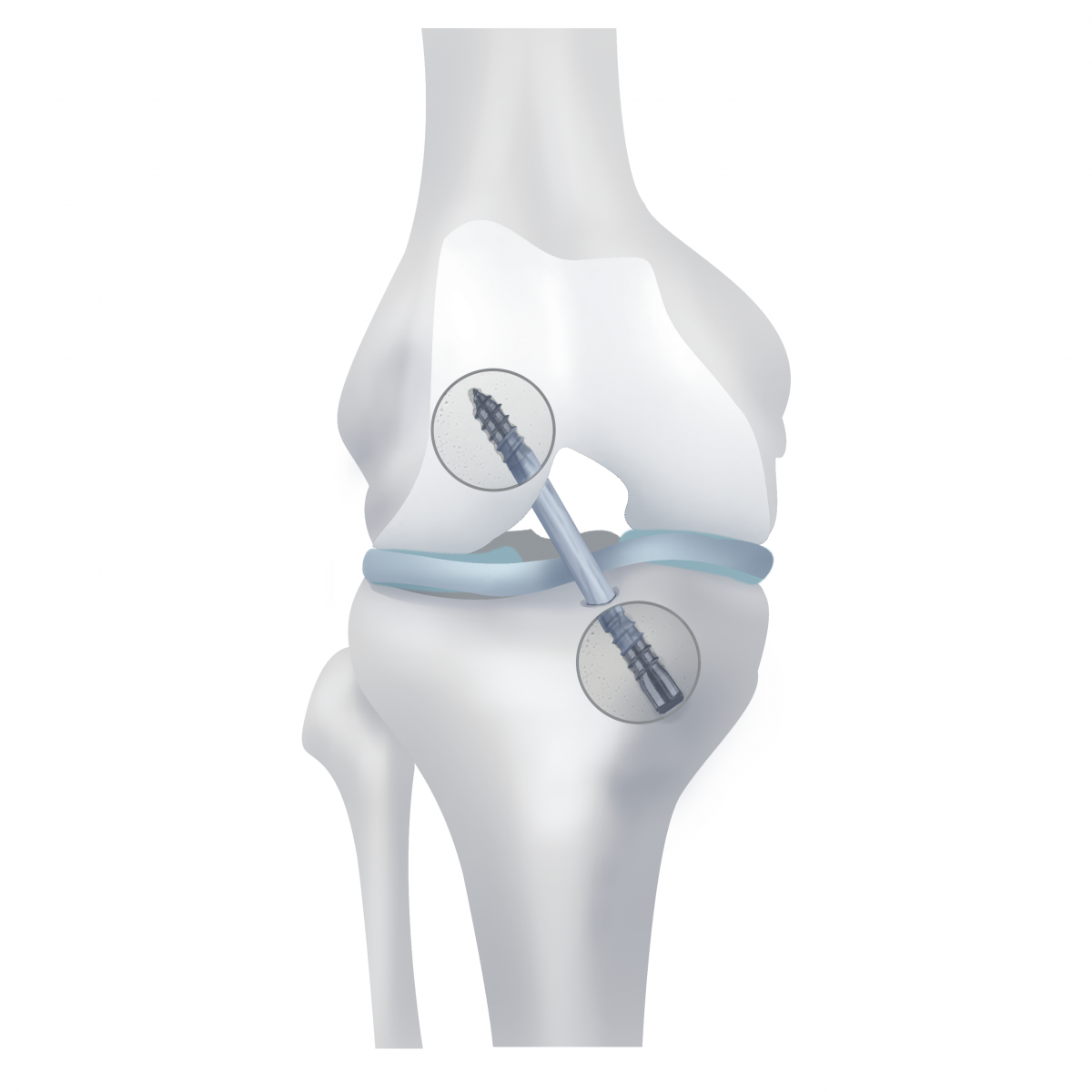
Fixation with an interference screw
- interference screw is twisted into the gap between the wall of the tunnel and graft femur and tibia, securely locks the graft to the bone over a large area;
- installing the top screw (thigh bone) is more technical;
- provide uniform strength of fixation of the graft;
- do not affect the location of the tunnels;
- over time (up to 3 years) disappear, turning into bone tissue.
In our clinic offers the advantage of the use of the graft tendon of the quadriceps femoris (QT) fixation with interference screws. It is technically more complicated technique, it requires the skill of surgeons and additional special equipment. In Ukraine, in addition to our clinic, rarely used. We have the technique perfectly, since it has many advantages over the others for the final result of the operation for the patient.
In patients with possible disruption of the microcirculation (Smoking, diabetes, etc.) and re-sculpting procedures PKS we use the BTB graft with two bone blocks.
Q: what is the period after injury is possible to do the operation?
In the absence of a pronounced inflammatory process and restrictions of movement in the joints in any period.
Question: is this a painful procedure?
The operation is painless thanks to the use in our clinic, the combined method of anesthesia: spinal anesthesia and blocking of nerve endings on the thigh. During surgical intervention introduces a sleeping pill. Postoperative analgesia is used according to need.
Question: how long is the operation?
The technical part of the replacement the PCB only lasts about 45 minutes.
Question: how much should you be in the hospital?
2 days.
Question: when may stepped on the foot after surgery?
Step on the operated leg with a partial load with the help of crutches is allowed on the next day after surgery. Crutches are used to unloading of the limb for 4 weeks after the operation.
Question: is fixed leg in a cast?
No. Uses removable retaining device (splint), which should be worn for 4 weeks at night and during the movement. If the limb is not loaded (the man sits or lies), the splint is not used.

Question: how soon after surgery can normally walk?
As a rule, the normal gait is restored within 6 weeks after surgery.
Question: when is allowed to drive a car?
- if operated by the left foot, a car with an automatic transmission you can use the next day after the operation;
- if operated by the right foot - 4 weeks after surgery for the restoration of full range of motion in the joint
- if a car with a manual transmission - 4 weeks after surgery for the restoration of full range of motion in the joint, regardless of which side of the operation.
Question: when can you return to sports?
- in the gym for comfort - 4 weeks after the operation;
- to swim WITHOUT the use of foot - 2.5 weeks after the operation;
- swim With the use of foot - 6 weeks after the operation;
- run - in 3 months after operation;
- exercise (play and contact sports) - after 4.5 months after surgery, after controlling for magnetic resonance imaging;
- complete recovery is possible after 6 months after the operation.
Question: what is the effectiveness of surgery?
If the operation is OK, restore the function of the knee joint and preliminary quality of life possible almost in 100% of cases.
However, there is no 100% guarantee any form of treatment.
According to our clinic, we obtained excellent and good results plastic surgery PCP in 96.2% of cases.
Satisfactory results - 3.2% of cases.
Unsatisfactory (resorption of the transplant, recurrence of instability) - 0.6%
The result depends on many components, which include:
- age and baseline health status of the patient
- the severity of the damage,
- the conditions of a medical institution,
- the skill and experience of the surgeon
- adequate postoperative process.
Thus, to do surgery for ACL reconstruction in specialized clinics definitely worth it.
Question: possible complications?
In our clinic, it was noted the following problems:
Reactive arthritis - inflammation in the knee joint in 2 - 3 weeks after surgery as a result of entering into the joint private microorganisms with undetected foci of chronic inflammation. Frequency - 1 in more than 50 operations. Treated with antibiotics.
Arthrofibrosis - the increase in terms of achieving full range of motion in the joint due to excessive formation of scar tissue. Treated with strengthening and rehabilitation exercises. In the absence of progression of range of motion after 4.5 months after operation, a dissection of scars with the help of arthroscopic surgery. The frequency of repeated operations - 1 in more than 50 operations.
Question: what are the advantages of treatment in the medical center "Orthopedics Ruslan Sergienko"?
- Center "Orthopedics Ruslan Sergienko":
- 10 years in the market of medical services in Ukraine
- 25 years of experience from leading experts (Ruslan Sergienko, PhD, Anna Vovchenko, PhD)
- study abroad
- full technical support operations
- the availability of all essential drugs and consumables
- modern operating with the technology of air-conditioning "clean air"
- 2 anesthesiologist who have mastered all the techniques of anesthesia;
- comfortable single rooms;
- meals restaurant type;preliminary calculation of the cost of the operation surcharges during hospital stay and at discharge.
ENTRUST THE CARE OF THEIR HEALTH REAL PROFESSIONALS!
Photo gallery:
Product rating is: 1 from 5
Please rate the product:
Advantages of treatment in Orthopedics by Ruslan Sergienko
-
10 years on medical services in Ukraine
-
> 25 years of experience with leading specialists
-
Anna Vovchenko and Ruslan Sergienko are recognized opinion leaders among the orthopedic traumatologists
-
> 150,000 consultations were held
-
> 7,500 surgeries were performed
-
All types of pain management
-
The operating unit is equipped according to international standards
-
Availability of all medicines and supplies
-
Single rooms, equipped with the characteristics of orthopedic patients
-
Three meals a day
-
Postoperative rehabilitation by certified specialists
-
Pricing Transparency
