The injury to the Achilles tendon
A full range of orthopedic services, from diagnosis to full recovery
Torn Achilles tendon.
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in a person. It is formed as a result of the fusion of the tendons of the calf and flounder muscles, and is attached to the hillock of the calcaneus.
When the muscles contract, they pull the Achilles tendon, and as a result, there is a plantar flexion in the ankle joint – that is, we can stand on the toe of the foot or jump, pushing off the feet.
There is a mucosal sac between the surface of the calcaneus and the tendon, which reduces the friction between the bone and the tendon. In addition, the tendon itself is located in a special channel, inside which there is also a little liquid that reduces friction.
The Achilles tendon can rupture in three cases:
1. Degenerative Theory
For the most part, the tendon consists of a special protein – collagen, which practically does not stretch. This protein forms the fibers of the tendon. In some cases, including due to hereditary reasons, the collagen becomes less strong (degenerative changes occur) and a rupture may occur.
Sometimes the collagen becomes so weak that the rupture can occur without any injury at all – in this case, they talk about a spontaneous rupture.
Drugs such as corticosteroids (diprospan, hydrocortisone) and fluoroquinolone antibiotics (ciprofloxacin) can contribute to degeneration. It is important to note that corticosteroids increase the risk of tendon rupture not only with local administration (for example, with injections for the treatment of tenopathies, inflammation of the mucous bags, etc.), but also with oral (in the form of tablets) or systemic (intravenous, intramuscular) administration in the treatment of various diseases.
Another reason degeneration is a chronic inflammation of the tendons, so-called senopati, tendinitis, etc.
2. Mechanical Theory.
The rupture can occur without degenerative changes. At the heart of this theory is the belief that any healthy tendon can break if a force greater than its strength is applied to it.
In particular, a tear can occur when the triceps muscle of the lower leg is uncoordinated (for example, when the outer head of the calf muscle begins to pull the tendon, and the inner one is delayed by a fraction of a second). This is possible if a person begins to exercise after a long break or if he gives too much load without warming up.
Therefore, the gap often occurs in the so-called "weekend athletes" of 30-50 years of age, who play sports irregularly, occasionally, neglect the warm-up and overestimate their physical capabilities.
In addition, microtrauma can also lead to degeneration, when as a result of repeated sprains, micro-tears of the tendon occur, and it becomes weaker.
3. Hyperthermic Theory.
The tendon is not an absolutely inextensible structure, it is characterized by elasticity (due to a special protein elastane). At least about 10% of the energy generated by elastic tendon elongation is converted into heat energy.
For example, after jogging for 7 minutes, the tendon can heat up to 45 degrees Celsius, and the destruction of tendon cells-tenocytes-can occur. Thus, hyperthermia that occurs during movement can also contribute to degenerative processes. A good blood supply allows the tendon to cool down, and if the blood supply is reduced, the tendon overheats.
Scientists believe that 30-50 years of age is at risk of rupture of the Achilles tendon also because with age, degenerative changes accumulate in the tendon, and age still predisposes a person to consider himself absolutely healthy in terms of sports, which can lead to an overestimation of his capabilities and injury.
Symptoms
Usually, when a tear occurs, a person feels a sudden pain, as if someone hit the back of the leg with a stick. Sometimes, at the moment of rupture, a person can hear the sound of the rupture itself, similar to a dry crack or crunch.
After this, the strength of the triceps muscle of the lower leg is sharply reduced – because the calf and flounder muscles are now not connected to the heel through the Achilles tendon and can not extend the foot. After that, there is swelling and a bruise may appear, which gradually increases in size over a few days and can go down to the fingertips.
If a person is not full, then in the course of the Achilles tendon at the place of its rupture, you can see or feel a trap, a pit.
As a rule, after a rupture of the Achilles tendon, a person can not straighten the foot. Gait is disturbed, there is a strong limp, and sometimes because of the pain, a person can not step on his foot at all.
What are the disadvantages of conservative treatment?
Together with the rupture of the tendon, the blood vessels are ruptured, and blood accumulates at the site of the rupture (hematoma), which prevents the ends of the torn tendon from coming together.
As a result, the tendon fuses with elongation, and its strength is significantly reduced. In addition, due to this hematoma, the tendon is fused by a scar, and not by tendon tissue. As a result, it becomes less strong and there is a high risk that a second break will occur in the future.
Large scientific studies show that the risk of re-rupture after conservative treatment is three times greater than after surgical treatment (surgical suturing of a torn tendon).
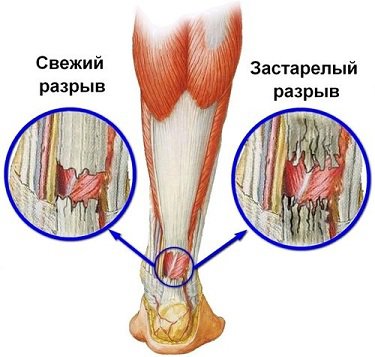
If the tendon rupture occurred against the background of degenerative changes in the tendon itself, the ends of the tendon are loosened, like a disheveled washcloth. With conservative treatment, such scars can not grow together firmly.
Conservative treatment is possible if it is started within a few hours after the rupture (while the ends of the tendon can still be matched), if the patient does not have functional requirements, does not intend not only to play sports, but also to lead any active lifestyle (for example, elderly people who move only around the apartment), and also if this is the first injury of the Achilles tendon.
In other cases, we consider it more justified to perform an operation that allows you to accurately and firmly sew the torn tendon (or perform plastic surgery if the suture is impossible), to get a more reliable and faster result.
ENTRUST THE CARE OF YOUR HEALTH TO REAL PROFESSIONALS!
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in a person. It is formed as a result of the fusion of the tendons of the calf and flounder muscles, and is attached to the hillock of the calcaneus.
When the muscles contract, they pull the Achilles tendon, and as a result, there is a plantar flexion in the ankle joint – that is, we can stand on the toe of the foot or jump, pushing off the feet.
There is a mucosal sac between the surface of the calcaneus and the tendon, which reduces the friction between the bone and the tendon. In addition, the tendon itself is located in a special channel, inside which there is also a little liquid that reduces friction.
The Achilles tendon can rupture in three cases:
- with a direct blow to a strained Achilles tendon. More often, this mechanism of injury occurs when playing sports, for example, when playing football;
- in case of indirect injury: as a result of a sharp contraction of the muscles of the lower leg when the leg is bent, examples:
- when trying to jump in basketball or volleyball;
- with an unexpected sharp back flexion of the foot – for example, when jumping from a ladder step;
- when falling from a height on the foot with the toe extended.
- Open tear-when wounded with a sharp object (for example, a knife or a scythe).
1. Degenerative Theory
For the most part, the tendon consists of a special protein – collagen, which practically does not stretch. This protein forms the fibers of the tendon. In some cases, including due to hereditary reasons, the collagen becomes less strong (degenerative changes occur) and a rupture may occur.
Sometimes the collagen becomes so weak that the rupture can occur without any injury at all – in this case, they talk about a spontaneous rupture.
Drugs such as corticosteroids (diprospan, hydrocortisone) and fluoroquinolone antibiotics (ciprofloxacin) can contribute to degeneration. It is important to note that corticosteroids increase the risk of tendon rupture not only with local administration (for example, with injections for the treatment of tenopathies, inflammation of the mucous bags, etc.), but also with oral (in the form of tablets) or systemic (intravenous, intramuscular) administration in the treatment of various diseases.
Another reason degeneration is a chronic inflammation of the tendons, so-called senopati, tendinitis, etc.
2. Mechanical Theory.
The rupture can occur without degenerative changes. At the heart of this theory is the belief that any healthy tendon can break if a force greater than its strength is applied to it.
In particular, a tear can occur when the triceps muscle of the lower leg is uncoordinated (for example, when the outer head of the calf muscle begins to pull the tendon, and the inner one is delayed by a fraction of a second). This is possible if a person begins to exercise after a long break or if he gives too much load without warming up.
Therefore, the gap often occurs in the so-called "weekend athletes" of 30-50 years of age, who play sports irregularly, occasionally, neglect the warm-up and overestimate their physical capabilities.
In addition, microtrauma can also lead to degeneration, when as a result of repeated sprains, micro-tears of the tendon occur, and it becomes weaker.
3. Hyperthermic Theory.
The tendon is not an absolutely inextensible structure, it is characterized by elasticity (due to a special protein elastane). At least about 10% of the energy generated by elastic tendon elongation is converted into heat energy.
For example, after jogging for 7 minutes, the tendon can heat up to 45 degrees Celsius, and the destruction of tendon cells-tenocytes-can occur. Thus, hyperthermia that occurs during movement can also contribute to degenerative processes. A good blood supply allows the tendon to cool down, and if the blood supply is reduced, the tendon overheats.
Scientists believe that 30-50 years of age is at risk of rupture of the Achilles tendon also because with age, degenerative changes accumulate in the tendon, and age still predisposes a person to consider himself absolutely healthy in terms of sports, which can lead to an overestimation of his capabilities and injury.
Symptoms
Usually, when a tear occurs, a person feels a sudden pain, as if someone hit the back of the leg with a stick. Sometimes, at the moment of rupture, a person can hear the sound of the rupture itself, similar to a dry crack or crunch.
After this, the strength of the triceps muscle of the lower leg is sharply reduced – because the calf and flounder muscles are now not connected to the heel through the Achilles tendon and can not extend the foot. After that, there is swelling and a bruise may appear, which gradually increases in size over a few days and can go down to the fingertips.
If a person is not full, then in the course of the Achilles tendon at the place of its rupture, you can see or feel a trap, a pit.
As a rule, after a rupture of the Achilles tendon, a person can not straighten the foot. Gait is disturbed, there is a strong limp, and sometimes because of the pain, a person can not step on his foot at all.
What are the disadvantages of conservative treatment?
Together with the rupture of the tendon, the blood vessels are ruptured, and blood accumulates at the site of the rupture (hematoma), which prevents the ends of the torn tendon from coming together.
As a result, the tendon fuses with elongation, and its strength is significantly reduced. In addition, due to this hematoma, the tendon is fused by a scar, and not by tendon tissue. As a result, it becomes less strong and there is a high risk that a second break will occur in the future.
Large scientific studies show that the risk of re-rupture after conservative treatment is three times greater than after surgical treatment (surgical suturing of a torn tendon).

If the tendon rupture occurred against the background of degenerative changes in the tendon itself, the ends of the tendon are loosened, like a disheveled washcloth. With conservative treatment, such scars can not grow together firmly.
Conservative treatment is possible if it is started within a few hours after the rupture (while the ends of the tendon can still be matched), if the patient does not have functional requirements, does not intend not only to play sports, but also to lead any active lifestyle (for example, elderly people who move only around the apartment), and also if this is the first injury of the Achilles tendon.
In other cases, we consider it more justified to perform an operation that allows you to accurately and firmly sew the torn tendon (or perform plastic surgery if the suture is impossible), to get a more reliable and faster result.
ENTRUST THE CARE OF YOUR HEALTH TO REAL PROFESSIONALS!
Product rating is: 2 from 5
Please rate the product:
Advantages of treatment in Orthopedics by Ruslan Sergienko
-
10 years on medical services in Ukraine
-
> 25 years of experience with leading specialists
-
Anna Vovchenko and Ruslan Sergienko are recognized opinion leaders among the orthopedic traumatologists
-
> 150,000 consultations were held
-
> 7,500 surgeries were performed
-
All types of pain management
-
The operating unit is equipped according to international standards
-
Availability of all medicines and supplies
-
Single rooms, equipped with the characteristics of orthopedic patients
-
Three meals a day
-
Postoperative rehabilitation by certified specialists
-
Pricing Transparency
