Femoro-acetabular conflict
A full range of orthopedic services, from diagnosis to full recovery
Femoroacetabular conflict (femoroacetabular impingement) is a pathomechanical process of chronic traumatization of the articular lip (acetabular lip) or the edge of the acetabular cavity by the head or neck of the femur.
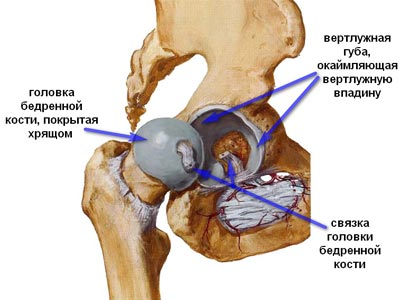
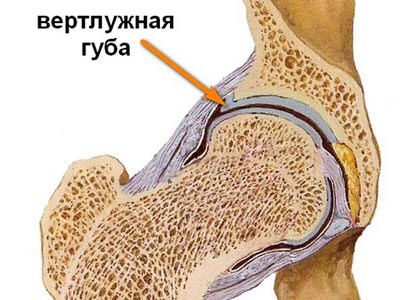
The cause of the conflict is various congenital or acquired disorders of the relationship between the femoral head and the acetabulum: a violation of their shape and configuration.
THERE ARE 3 TYPES OF FEMOROACETABULAR CONFLICT:
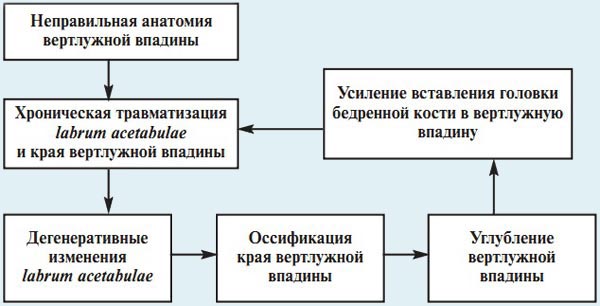
1. Acetabular type of conflict (pincer) - characterized by an irregular anatomy of the acetabulum with an unchanged proximal femur.
In this variant of the conflict, the acetabulum overlaps too much, as if it hangs over the head of the femur, and when bending in the hip, both the articular lip filling the cavity and the cartilage covering the head of the femur are injured. The acetabular type occurs more often in young and middle-aged women. Predisposing factors are an increase in the anteversion of the acetabulum, coxa profunda, retroversion of the acetabulum (as a manifestation of dysplasia), and acquired-protrusion of the bottom of the acetabulum, protruding anterior-upper edge of the acetabulum, retroversion of the acetabulum (as a consequence of injury).
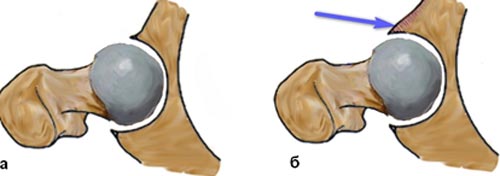
a normal hip joint: movement of the head in the acetabulum do not interfere;
b - Pincer type of conflict: the movement prevents Vetlugina lip
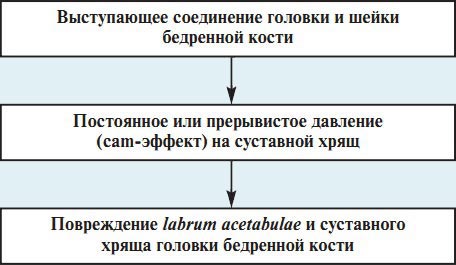
2. Femoral conflict type (cam) - movement is hindered by a deformity at the base of the femoral head Femoral conflict type (cam) - characterized by an irregular morphology of the junction of the head and neck of the femur with an unchanged acetabulum.
In this variant of the conflict, there is a thickening on the neck of the femur (a bump, an outgrowth) and when moving, the femur, inserted into the unchanged acetabulum, injures the articular lip.
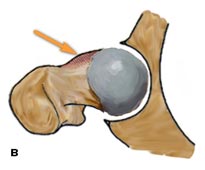
in-cam type:the movement is hindered by the deformation at the base of the head
of the femur.
The femoral type is more likely to develop in young men.
The cause of thickening on the femoral neck is either congenital factors: the elliptical shape of the femoral head, the protruding connection of the head and neck of the femur, or acquired-epiphyseolysis, Perthes ' disease, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, the consequences of fractures of the acetabulum.
3. Mixed type of conflict - occurs most often, in about 86% of patients with femoroacetabular conflict.
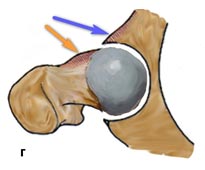
d-mixed type: movement is hindered by a deformity at the base of the femoral head and the acetabulum
MECHANISM OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ACETABULAR TYPE OF CONFLICT
THE MECHANISM OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE FEMORAL TYPE OF CONFLICT
SYMPTOMS OF FEMOROACETABULAR CONFLICT
(THE IMPINGEMENT OF THE HIP JOINT):
(HIP IMPINGEMENT)
Clinical examination and special diagnostic tests performed by the doctor. Diagnostic tests should be performed by a doctor who has certain skills, a good knowledge of anatomy, and experience in performing on a large number of patients. The diagnostic information content of some tests is very high and allows you to suspect femoroacetabular impingement with 80-90% confidence even before using X-ray or MRI diagnostics.
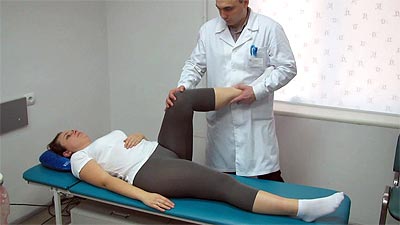
The most sensitive is the impeachment test - the occurrence of pain during flexion and internal rotation of the hip.
Additional tests may include:
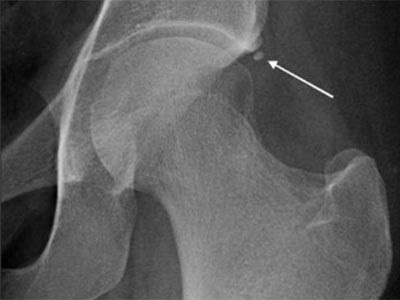
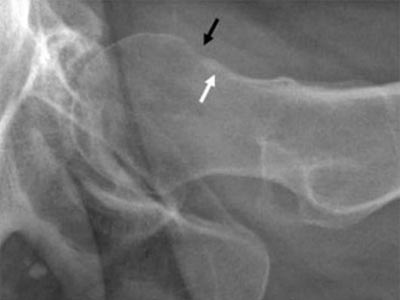
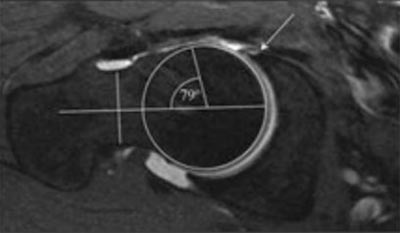
MRI examination, in addition to the signs that we see on radiographs, helps us to assess the presence of free fluid in the joint cavity, as well as damage to the soft tissue components of the joint.
TREATMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR CONFLICT
(TO IMPINGEMENT OF THE HIP JOINT)
Treatment of femoroacetabular conflict can be both conservative and operative.
Conservative treatment consists in the patient's compliance with the regime of painless loads, anti-inflammatory treatment in case of exacerbation, taking chondroprotectors and undergoing a course of physiotherapy procedures. Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma into the hip joint ("growth factors", PRP) provide a very good clinical effect.
However, the main method of treating femoroacetabular impingement is surgical intervention, since only in this case it is possible to permanently get rid of the causes of the conflict and their consequences. To date, the most modern method of surgical treatment of femoroacetabular conflict is hip arthroscopy. With the help of arthroscopy, we can perform the following manipulations: eliminate the growth on the femoral neck by performing plastic surgery of the femoral neck, you can also perform resection of the overhanging edge of the articular cavity, sew or remove damaged parts of the articular lip, treat articular cartilage, remove the formed exostoses and cysts, etc.
With untimely or inadequate treatment, femoroacetabular conflict leads to the early development of hip arthrosis, and this is a more serious disease, the result of which can be the replacement of the affected joint with an artificial one.
WHAT AFFECTS THE RESULTS OF HIP ARTHROSCOPY?
For high-quality hip arthroscopy and obtaining the most successful results, 3 conditions are necessary:


The cause of the conflict is various congenital or acquired disorders of the relationship between the femoral head and the acetabulum: a violation of their shape and configuration.
THERE ARE 3 TYPES OF FEMOROACETABULAR CONFLICT:
1. Acetabular type of conflict (pincer) - characterized by an irregular anatomy of the acetabulum with an unchanged proximal femur.
In this variant of the conflict, the acetabulum overlaps too much, as if it hangs over the head of the femur, and when bending in the hip, both the articular lip filling the cavity and the cartilage covering the head of the femur are injured. The acetabular type occurs more often in young and middle-aged women. Predisposing factors are an increase in the anteversion of the acetabulum, coxa profunda, retroversion of the acetabulum (as a manifestation of dysplasia), and acquired-protrusion of the bottom of the acetabulum, protruding anterior-upper edge of the acetabulum, retroversion of the acetabulum (as a consequence of injury).

a normal hip joint: movement of the head in the acetabulum do not interfere;
b - Pincer type of conflict: the movement prevents Vetlugina lip
2. Femoral conflict type (cam) - movement is hindered by a deformity at the base of the femoral head Femoral conflict type (cam) - characterized by an irregular morphology of the junction of the head and neck of the femur with an unchanged acetabulum.
In this variant of the conflict, there is a thickening on the neck of the femur (a bump, an outgrowth) and when moving, the femur, inserted into the unchanged acetabulum, injures the articular lip.

in-cam type:the movement is hindered by the deformation at the base of the head
of the femur.
The femoral type is more likely to develop in young men.
The cause of thickening on the femoral neck is either congenital factors: the elliptical shape of the femoral head, the protruding connection of the head and neck of the femur, or acquired-epiphyseolysis, Perthes ' disease, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, the consequences of fractures of the acetabulum.
3. Mixed type of conflict - occurs most often, in about 86% of patients with femoroacetabular conflict.

d-mixed type: movement is hindered by a deformity at the base of the femoral head and the acetabulum
MECHANISM OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ACETABULAR TYPE OF CONFLICT

THE MECHANISM OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE FEMORAL TYPE OF CONFLICT

SYMPTOMS OF FEMOROACETABULAR CONFLICT
(THE IMPINGEMENT OF THE HIP JOINT):
- pain in the groin
- pain over the trochanter with radiation on the outer surface of the thigh
- pain during flexion and internal rotation of the thigh
- start after a minor injury
- the pain increases after a long stay in a sitting position or after a significant load on the hip joint
- pain is directly proportional to the load on the hip joint
- patients younger than traditional patients with coxarthrosis
(HIP IMPINGEMENT)
Clinical examination and special diagnostic tests performed by the doctor. Diagnostic tests should be performed by a doctor who has certain skills, a good knowledge of anatomy, and experience in performing on a large number of patients. The diagnostic information content of some tests is very high and allows you to suspect femoroacetabular impingement with 80-90% confidence even before using X-ray or MRI diagnostics.

The most sensitive is the impeachment test - the occurrence of pain during flexion and internal rotation of the hip.
Additional tests may include:
-
Apprehension test – test for a premonition of danger) - pain during extension and external rotation;
FABER test-the patient is lying on his back, legs bent at the knees, the soles of his feet touching each other. The doctor puts a little pressure on his knees, trying to bring them closer to the bed. Then the vertical distance from the knees to the bed is measured. The test is considered positive if the vertical distance from the knee to the couch on the affected side is greater;
asymmetry of the external rotation – on the damaged side, the external rotation will be less.


MRI examination, in addition to the signs that we see on radiographs, helps us to assess the presence of free fluid in the joint cavity, as well as damage to the soft tissue components of the joint.

TREATMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR CONFLICT
(TO IMPINGEMENT OF THE HIP JOINT)
Treatment of femoroacetabular conflict can be both conservative and operative.
Conservative treatment consists in the patient's compliance with the regime of painless loads, anti-inflammatory treatment in case of exacerbation, taking chondroprotectors and undergoing a course of physiotherapy procedures. Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma into the hip joint ("growth factors", PRP) provide a very good clinical effect.
However, the main method of treating femoroacetabular impingement is surgical intervention, since only in this case it is possible to permanently get rid of the causes of the conflict and their consequences. To date, the most modern method of surgical treatment of femoroacetabular conflict is hip arthroscopy. With the help of arthroscopy, we can perform the following manipulations: eliminate the growth on the femoral neck by performing plastic surgery of the femoral neck, you can also perform resection of the overhanging edge of the articular cavity, sew or remove damaged parts of the articular lip, treat articular cartilage, remove the formed exostoses and cysts, etc.
With untimely or inadequate treatment, femoroacetabular conflict leads to the early development of hip arthrosis, and this is a more serious disease, the result of which can be the replacement of the affected joint with an artificial one.
WHAT AFFECTS THE RESULTS OF HIP ARTHROSCOPY?
For high-quality hip arthroscopy and obtaining the most successful results, 3 conditions are necessary:
-
sufficient level of equipment for performing arthroscopy.It is necessary to have a full set of expensive high-tech equipment: a camera with 30 and 70 degree optics, a light source, a pump, necessarily a shaver with different attachments, an ablator, a monitor, an EOP, a traction table. The absence of at least one of the above makes it impossible to perform a high-quality arthroscopy of the hip joint.
- An experienced orthopedic surgeon. Hip arthroscopy is a technologically more complex operation than, for example, knee and even shoulder arthroscopy. We can say that this is aerobatics even for an experienced orthopedic surgeon engaged in arthroscopy of the joints.
- Adequate anaesthetic support
Product rating is: 0 from 5
Please rate the product:
Advantages of treatment in Orthopedics by Ruslan Sergienko
-
10 years on medical services in Ukraine
-
> 25 years of experience with leading specialists
-
Anna Vovchenko and Ruslan Sergienko are recognized opinion leaders among the orthopedic traumatologists
-
> 150,000 consultations were held
-
> 7,500 surgeries were performed
-
All types of pain management
-
The operating unit is equipped according to international standards
-
Availability of all medicines and supplies
-
Single rooms, equipped with the characteristics of orthopedic patients
-
Three meals a day
-
Postoperative rehabilitation by certified specialists
-
Pricing Transparency
