Rotator / rotator cuff injury
A full range of orthopedic services, from diagnosis to full recovery
WHAT IS A ROTATOR CUFF AND WHAT IS IT USED FOR?
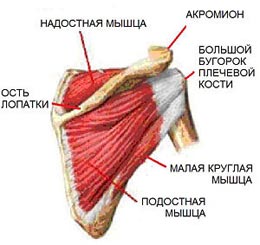
Rotational (rotator) cuff of the shoulder includes the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and small round muscles. These muscles are necessary to stabilize the head of the humerus and prevent its displacement when moving in the joint. In addition, these muscles allow you to perform rotational movements in the shoulder in all directions.
The scapular muscle rotates the arm inwards, the supraspinatus muscle raises the shoulder and "anchors" it, i.e. presses the head of the humerus into the articular cavity of the scapula when the shoulder is pulled sideways. In this case, the main force of withdrawal is determined by the deltoid muscle, and the supraspinatus muscle works as a commander directing the efforts of the deltoid muscle. The subacute muscle rotates the shoulder outward, and the small round muscle rotates outward and brings the arm to the torso. Damage to at least one of the four muscles leads to a sharp restriction of movement and loss of function of the shoulder joint.
CAUSES OF DAMAGE OR RUPTURE OF THE ROTATIONAL (ROTATOR)) SHOULDER CUFFS:
Damage to the rotator cuff of the shoulder can occur as a result of acute trauma. In this case, patients often describe a specific injury, after which pain appeared and the function of the shoulder was disrupted.
In some cases, a rotator cuff tear is the result of chronic microtraumatization of the muscles. Most often, this occurs in individuals whose professional activities are associated with frequent elevated hand positions or throwing movements. For example, athletes in sports such as baseball, tennis, weightlifting, and rowing. Constant microtraumatization of the rotator cuff tendons when hitting the ball, serving, throwing can lead to micro-tears of the muscle fibers, the muscles gradually thin out and over time, even with a minor injury, can easily tear.
A predisposition to overstrain of the rotator cuff tendons is found in teachers who write with chalk on a blackboard with their hand raised, in painters who paint walls, in builders, etc . In some patients, a rotator cuff tear may be a consequence of the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the muscles associated with aging, for example, in the elderly or a genetic predisposition.
TYPES OF DAMAGE OR RUPTURES OF THE ROTATIONAL (ROTATOR)) SHOULDER CUFFS:
Due to the cause of the rupture – traumatic or degenerative ruptures. According to the nature of the damage, partial and complete ruptures are distinguished. Partial tears do not pass through the entire thickness of the tendon, full ones extend to the entire thickness of the cuff layers. Traumatic injuries are divided into fresh, stale and old.
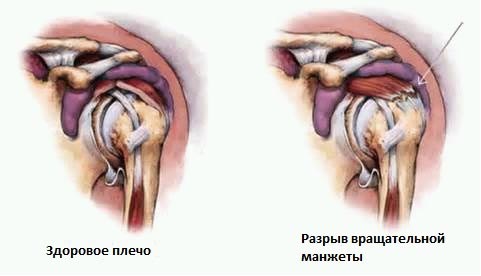
SYMPTOMS OF DAMAGE TO THE ROTATOR (ROTATOR)) SHOULDER CUFFS:
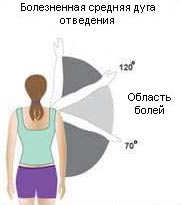
Signs of damage to the rotator cuff of the shoulder are pain and weakness in the withdrawal of the arm or external rotation of the shoulder.
The pain increases in certain phases of movement, especially when the hand is withdrawn
at an angle of 70 to 120°.
DIAGNOSIS OF ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES:
Diagnostic tests:
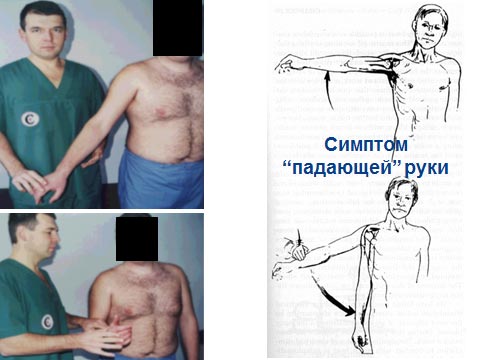
To diagnose damage to the rotator cuff of the shoulder, special tests are used, in which the doctor, bringing the patient's hands to a certain position, evaluates the motor ability of the damaged hand, observes the patient's reaction to their actions. The most informative tests are for the weakness of the abduction and the weakness of the external rotation of the shoulder. With extensive damage to the rotator cuff, symptoms of a falling arm (the patient can not hold the passively withdrawn arm) and lifting of the upper arm when trying to withdraw the arm (Leclerc's symptom) are also characteristic.
Ultrasound diagnostics
MRI examination
X-ray examination
TREATMENT OF ROTATOR CUFF INJURY:
Treatment of damage to the rotator cuff of the shoulder can be conservative and operative. Conservative treatment is indicated for partial injuries, when there is hope for the restoration of function without surgery. Conservative treatment is carried out along with the immobilization of the shoulder joint with a special bandage (orthosis), and includes:
physiotherapy procedures, the use of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, with severe pain – blockade with extended-acting glucocorticoids. Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma into the shoulder joint ("growth factors", PRP) provide a very good clinical effect.
If the duration of unsuccessful conservative treatment exceeds 2-3 months, it is necessary to raise the question of surgery.
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF ROTATOR (ROTATOR) INJURIES) SHOULDER CUFFS:
Repairing a torn rotator cuff tendon is a fairly complex operation. Reconstruction of the rotator cuff can be performed either by an open method, through an incision on the shoulder, or by an arthroscopic method. The disadvantages of open surgery are the need for large, traumatic incisions on the shoulder to provide access to the damaged tendons, which carries a high risk of side effects, long recovery after surgery.
In our Medical Center, surgical treatment of rotator cuff injuries is performed in a modern way, without incision of the joint - under arthroscopic control. Instead of an incision, local mini-punctures are performed, in one of which an arthroscope with a video camera is inserted, and in the other tools for performing the operation. The image from the video camera in the enlarged scale is transmitted to the video monitor, which allows the doctor to examine in detail all the structures of the joint and identify the location of the damage.
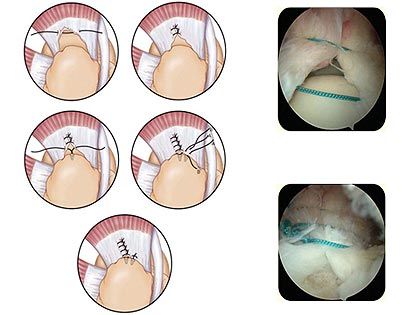
The essence of arthroscopic surgery is that the tear is stitched, and if there was a separation of the tendon from the place of fixation, then the suture is performed using special "anchor" fixators.
At the first stage of the operation, the joint is cleaned - the removal of all non-viable, degeneratively altered tissues of the rotator cuff. Then, the area of the humerus where the rotator cuff was torn or torn off is cleaned of the remaining soft tissues in order for the tendon to grow better to it. Usually to fix a torn tendon requires 2-3 anchor fixture. The retainer consists of an anchor and threads. The anchor is attached to the bone, and the threads in turn are sewn through the tendon.
The choice of the specific type of anchor retainer is made by the operating surgeon, but in general the patient should also be informed about which retainer is planned for use in his case. We recommend using retainers from world-renowned companies that have long proven themselves.
REHABILITATION AFTER SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY:
Properly performed surgery allows you to quickly start active rehabilitation, to prevent the development of complications and optimize the recovery time.
After arthroscopy of the shoulder, the arm is immobilized in the withdrawal position for several weeks with a special splint. This immobilization reduces the tension of the tendons and reduces the risk of re-rupture, creating favorable conditions for better healing of the tendon. The duration of immobilization is determined by the surgeon who performed the operation, since only he can assess the condition of the tendons and the strength of the suture performed.
From the first weeks after shoulder arthroscopy, patients are recommended to perform special exercises aimed at developing movements in the shoulder joint. However, their intensity and priority should be selected by the operating doctor and an experienced rehabilitologist.
In our Medical Center, patients after shoulder arthroscopy are offered a whole range of rehabilitation measures. The rehabilitation program is selected individually and includes:
Special exercises and physical therapy at the rehabilitation specialists of our Medical Center by the method of kinesiotherapy. Exercises are aimed at improving the volume of movement in the joint, preventing the development of contractures, increasing strength and endurance in the muscles of the shoulder girdle. The exercises are selected individually and performed on professional equipment in the rehabilitation hall, under the supervision of experienced rehabilitation instructors. Part of the exercises is signed to the patient for carrying out at home.

Physical therapy on the professional equipment of the BTL company: magnetic therapy, ultrasound therapy with the introduction of drugs, electrotherapy-reduce pain and swelling in the operated shoulder, prevent the formation of adhesions and scars, promote better healing, restore muscle tone.
ENTRUST THE CARE OF YOUR HEALTH TO REAL PROFESSIONALS!
Product rating is: 0 from 5
Please rate the product:
Advantages of treatment in Orthopedics by Ruslan Sergienko
-
10 years on medical services in Ukraine
-
> 25 years of experience with leading specialists
-
Anna Vovchenko and Ruslan Sergienko are recognized opinion leaders among the orthopedic traumatologists
-
> 150,000 consultations were held
-
> 7,500 surgeries were performed
-
All types of pain management
-
The operating unit is equipped according to international standards
-
Availability of all medicines and supplies
-
Single rooms, equipped with the characteristics of orthopedic patients
-
Three meals a day
-
Postoperative rehabilitation by certified specialists
-
Pricing Transparency
